What Does Your Dog’s Tail Movement Mean? A Guide to Canine Communication

Your dog's tail movements are more than just wags—they're a window into their emotions. A high tail shows confidence and happiness, while a low or tucked tail suggests fear or submission. Fast wags mean excitement; slow ones can hint at relaxation or insecurity. If the wag is vigorous and broad, your dog likely feels friendly and content. Direction matters too: right-side wags point to happiness, and left-side wags may reveal anxiety. Different breeds, like Labradors and Rottweilers, have their unique expressions. Even tailless dogs communicate emotions with ears and facial cues. Uncover more about this fascinating canine language.
Tail Position and Emotions
When observing a dog, pay close attention to its tail position, as it reveals a lot about its emotions. The tail's position serves as a key indicator of the dog's emotional state. For instance, a high tail usually signals confidence and happiness, reflecting positive feelings. In contrast, a low or tucked tail typically indicates fear or submission, pointing to negative feelings. Understanding these body language cues can help you better interpret what your dog might be experiencing.
Tail wagging also plays a significant role in conveying your dog's emotions. When a dog wags its tail to the right side, it often shows joy or excitement—definitely positive feelings. Conversely, if the tail wags more to the left, it might suggest fear or anxiety, which are negative emotions. A tail held straight out horizontally often signifies curiosity and interest in the surroundings, offering a neutral or inquisitive emotional state.
Different tail movements provide important context about how your dog feels. By interpreting these cues, you can respond more appropriately to your dog's needs, ensuring a better understanding and stronger bond between you and your furry friend.
Speed of Tail Wagging
The speed of a dog's tail wagging is a fascinating aspect of canine communication that reveals much about their emotions. When your dog wags its tail quickly, it's often a sign of high excitement and positive emotions like happiness or enthusiasm to engage. You'll notice that the faster the wag, the more intense the dog's emotional state. This is where tail cues become crucial; they help you understand what your dog might be feeling.
However, not all tail movements are the same. A slow wag might suggest your dog is relaxed, but it could also mean they're feeling insecure or cautious as they assess their surroundings. It's significant to take into account the context in which the tail is wagging. For instance, a vigorous, broad wag often means friendliness and contentment. On the other hand, a stiff, narrow wag may indicate your dog is alert or defensive.
The higher the tail, the faster the wagging could be, and this combination often works well to express how your dog is feeling. By paying attention to these tail cues, you can better interpret your dog's emotional state and respond accordingly.
Directional Tail Wag Analysis

Directional tail wag analysis offers intriguing insights into a dog's emotional state by focusing on the direction their tail wags. When your canine companion's tail wags to the right side, it usually signals positive emotional responses. This type of tail movement suggests your dog is feeling happy, confident, and enthusiastic to engage socially. It's an indication that your furry friend perceives the environment as friendly or familiar. On the other hand, if the tail wags to the left side, it may reflect negative emotions such as fear or anxiety. This left-side tail wagging often indicates discomfort or unease.
The science behind this behavior involves the lateralization of brain function. The left hemisphere of a dog's brain controls movements on the right side of their body, which is associated with positive emotions. Conversely, the right hemisphere manages movements on the left side, linked to negative emotional responses. By observing the directionality of tail wagging, you can gain valuable insights into your dog's emotional state. This understanding improves dog communication, allowing you to respond effectively to your dog's needs and enrich your interactions. Paying attention to your dog's tail movement is key to fostering a better relationship.
Breed-Specific Tail Behaviors
Dog breeds showcase unique tail behaviors, shaping how they communicate emotions. Long-tailed breeds often have the advantage in communication. For instance, Labradors are famous for their broad, wagging tails, signaling friendliness and excitement. In contrast, Rottweilers, with their more rigid tail movements, tend to display a more assertive demeanor. These differences highlight how breed-specific tail behaviors can influence the way dogs express themselves.
For breeds like the Basenji, tail curls play an important role in their communication. The angle and position of the curl can convey different emotional states, adding a layer of complexity to their body language. On the other hand, breeds with docked tails, such as some Terriers, might face challenges in using their tails for communication. They often rely more on other body language signals, like ear position and facial expressions, to convey their emotions effectively.
Tail length and shape also play a significant role. A wagging tail on a Greyhound may mean something different than the same movement on a Bulldog due to their distinct tail characteristics. Understanding these breed-specific tail behaviors helps you better interpret your dog's emotions and communication.
Asymmetric Tail Movements
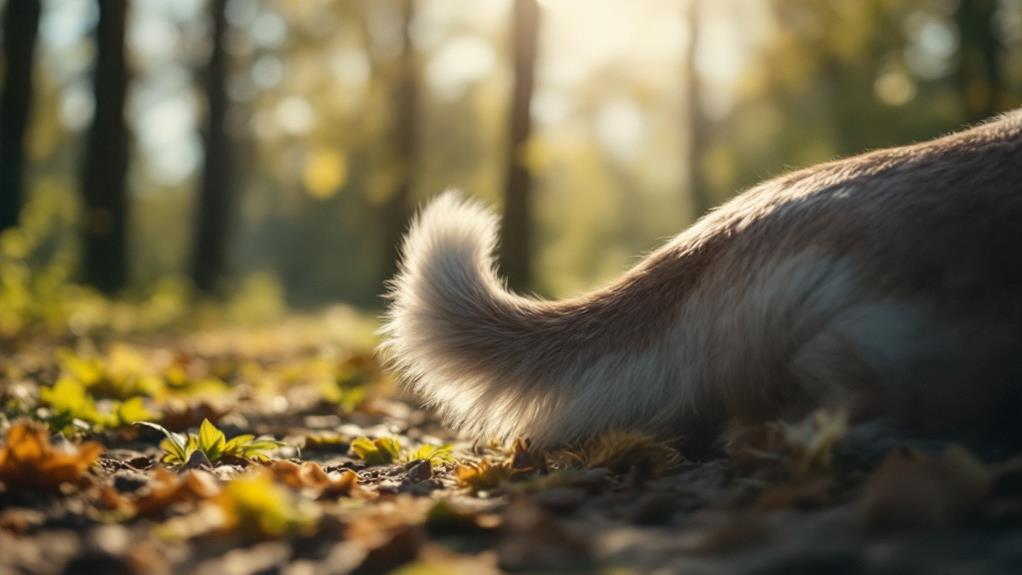

Among the fascinating aspects of canine communication is the phenomenon of asymmetric tail movements. When observing your dog's tail wag, you'll notice that it doesn't just swing randomly. In fact, these movements can reveal a lot about your dog's emotional responses. Dogs communicate their feelings through the direction of their tail wags. Research shows that right-side wagging is typically associated with a happy dog and positive feelings. This directional preference reflects the lateralization of brain function in your furry friend.
Conversely, you'll notice that left-side tail movements often occur when your dog encounters something unfamiliar or potentially threatening. Such wagging highlights the more negative emotions dogs might be experiencing during these canine interactions. When your dog is uncomfortable, the intensity and frequency of their tail wagging might decrease, indicating stress or apprehension.
Understanding these asymmetric tail movements can greatly improve how you interact with your dog. Recognizing a right-sided wag in familiar and comforting environments helps you confirm your dog's ease and contentment. Meanwhile, identifying left-sided wags can alert you to situations where your dog might feel uneasy, allowing you to address their needs more effectively. Your dog's tail demonstrates more than just wagging—it's a window into their emotional world.
Tail Signals in Social Contexts
Understanding your dog's tail movements goes beyond simply observing which side the wag favors. Tail wags play a vital role in social interactions, serving as a telltale sign of your dog's emotions. A right-side wag often indicates happiness, suggesting your dog might be excited to approach other dogs or familiar people. Conversely, a left-side wag can reflect discomfort or anxiety, especially around unfamiliar dogs. Recognizing these subtle cues helps you interpret your dog's body language accurately and guarantee safe social exchanges.
In addition to direction, the position and speed of the wagging tail mean different things:
- High, fast wagging tail: This usually signals excitement and a willingness to engage, perfect for when your dog is enthusiastic to meet new friends.
- Low, slow wag: This can indicate caution or fear, suggesting your dog is trying to assess the situation before diving in.
- Docked or short tails: Dogs with limited tail mobility might face challenges in expressing their emotions, leading to potential misunderstandings.
Communication in Tailless Dogs

Without the expressive tool of a tail, tailless dogs rely heavily on alternative forms of body language to communicate their emotions. You'll notice that these dogs use their ears, facial expressions, and comprehensive body posture to convey what they're feeling. This means you should pay close attention to these cues to understand their emotional state accurately.
For a tailless dog, a relaxed body, loose posture, and soft facial expression often indicate feelings of trust and contentment. Conversely, tense muscles or pinned back ears might suggest anxiety or discomfort. These dogs have mastered using every part of their body for communication, making it all the more significant for you to observe their signals closely.
Approaching tailless dogs requires a bit of caution. Without the usual tail signals, it's easy to misinterpret their emotions, leading to misunderstandings. Always look at their whole body language and facial expressions to gauge their comfort level. Understanding these signals is vital not just for your interactions but also for their communication with other dogs. By recognizing the subtle cues in a tailless dog's body language, you foster better communication and build a stronger bond of trust.
Tail and Body Language Correlation
A dog's tail and body language work together to create a thorough communication system, revealing their emotional state and intentions. By observing tail position, tail wagging, and body posture, you can better understand what your dog is trying to communicate. High tails often indicate confidence, while low or tucked tails suggest fear or submission. This is vital during dog training, as reading these signals helps you respond appropriately.
Tail wagging offers further insights. Fast wags typically show excitement, while the direction can indicate emotions: right-side wagging is often linked to positive feelings, while left-side wagging may signal anxiety. Coupled with body posture, these cues are even more telling. A relaxed dog has loose body posture and bright eyes. In contrast, aggressive dogs might display stiff bodies and high, rigid tails, alerting you to potential threats.
Understanding this communication is fundamental for creating a safe environment for your dog. Consider these aspects:
- Tail Position: High or low tail positions signal different emotions.
- Tail Wagging: Speed and direction provide context.
- Body Posture: Complements tail signals, indicating general mood.
Being attentive to these signals improves your bond and keeps interactions positive.
Playful Tail Behaviors
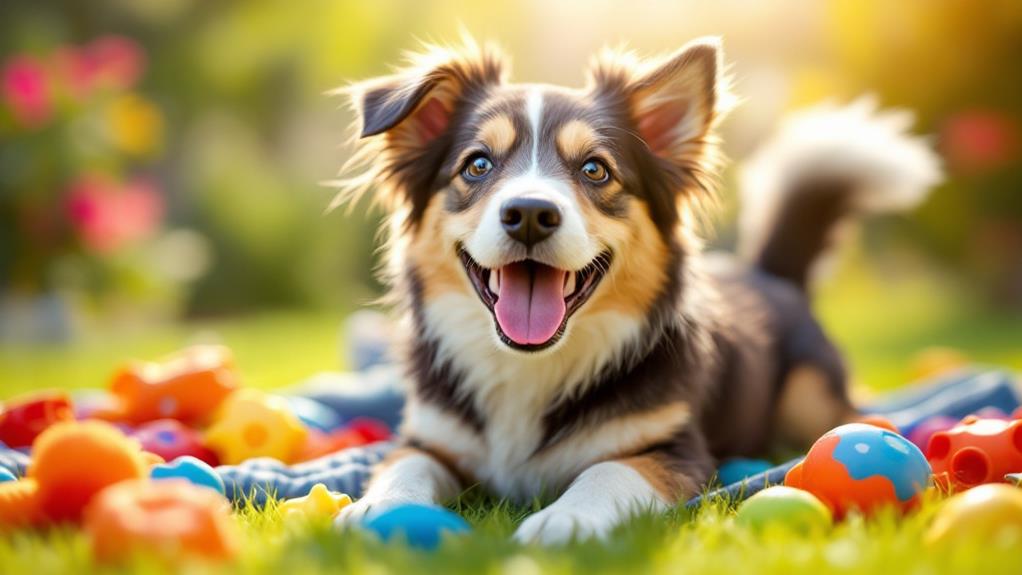

Picture your dog's tail swishing in wide, circular motions like a gentle propeller—this playful tail behavior often signals happiness and relaxation. When you see this kind of tail wagging, your dog is likely feeling content and at ease, especially during interactions with familiar dogs or people. It's a clear indicator that your furry friend is ready for some fun.
A common playful gesture is the play bow, where your dog stretches its front legs forward and keeps its rear end raised. This position is often paired with vigorous tail wagging, signaling an invitation to engage in play. These tail movements show your dog's excitement and enthusiasm to interact.
During playtime, rapid tail wagging might accompany quick bursts of movement or pouncing behavior, highlighting your dog's friendly intentions. Dogs often take turns in play, showcasing their social skills. As they do, their tails wag freely and energetically, indicating their enjoyment and engagement.
The variety in your dog's tail movements during playtime—from broad wags indicating contentment to fast wags displaying high energy levels—contributes to a positive and enjoyable atmosphere. Recognizing these cues helps you understand your dog's playful mood.
Emotional Insights From Tail Movement
While observing your dog's playful tail behaviors, you might wonder what deeper emotions are being communicated. Dogs wag their tails for numerous reasons, providing valuable insights into their emotional state. The direction of the wag can be a key indicator. Right-side tail wags often mean your dog is happy and confident, while left-side wags may signal fear or anxiety. Understanding these can significantly improve your canine communication skills.
The speed and position of tail wags also reveal crucial emotional information. A high, fast wag typically indicates excitement and a high level of arousal, suggesting your dog is happy and ready to engage. Conversely, a slow, low wag might suggest insecurity or submission, showing a calmer or uncertain emotional state.
To better interpret your dog's tail movement, consider these points:
- Direction of the Wag: Right-side for positive emotions, left-side for negative ones.
- Speed of Tail Wags: Faster wags reflect higher excitement; slower ones indicate calmness.
- Social Context: Dogs may change their wagging based on familiarity and emotional context, affecting interactions.
Mastering these insights can improve your relationship and enhance training by preventing misunderstandings or unwanted behavior.